What’s the Difference Between a Deep Plane Facelift and Traditional Facelift?
Concerns about looking “pulled” or unnatural after facelift surgery are common among individuals, who have likely witnessed celebrities, news anchors, or individuals in their own communities with obvious signs of having undergone a traditional facelift.
One reason for this phenomenon is that the most frequently performed facelift procedure, known as a SMAS plication lift, is a superficial technique that involves lifting the skin and suturing the SMAS without elevating or releasing the deeper structures of the face and neck. While this method is an improvement over skin-only lifting, separating the skin from the underlying muscles can create a taut, unnatural appearance. Moreover, this method only addresses the lower third of the face and jawline and does not lift sagging cheeks.

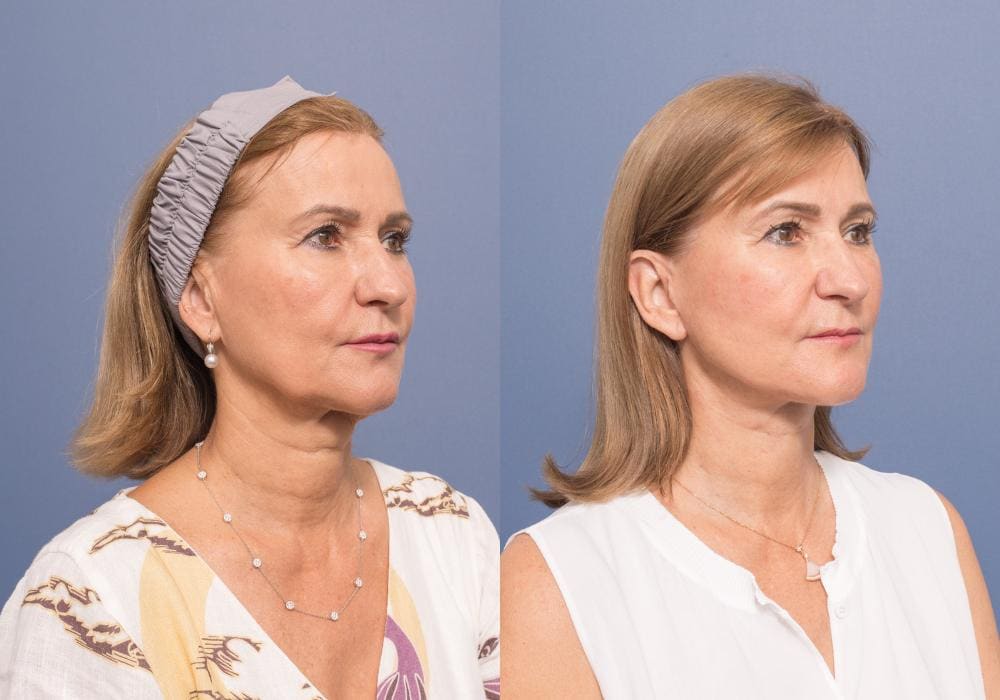
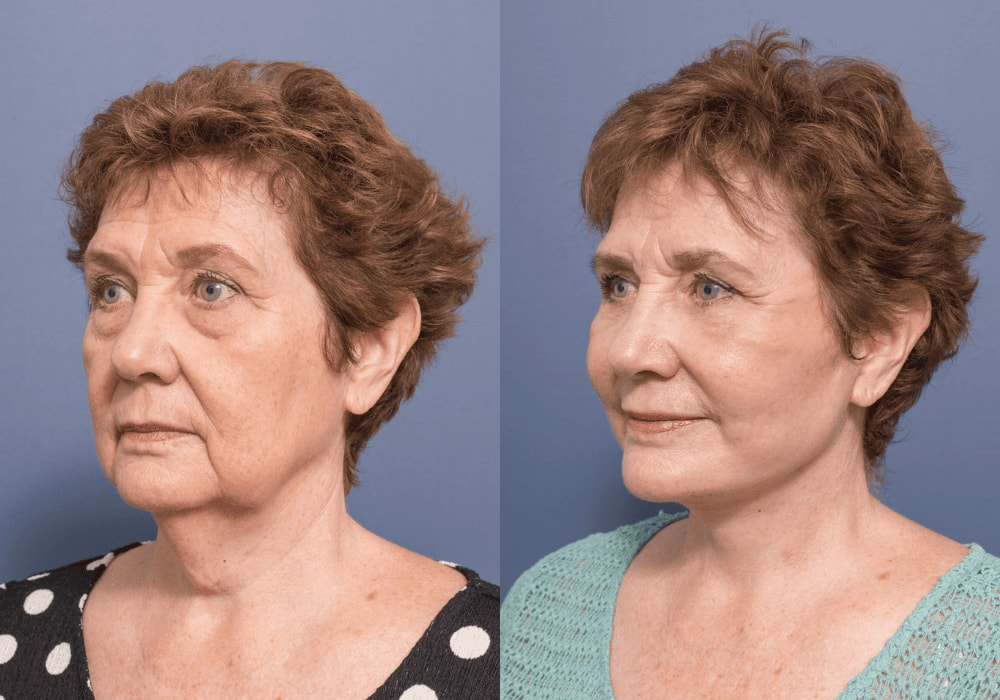
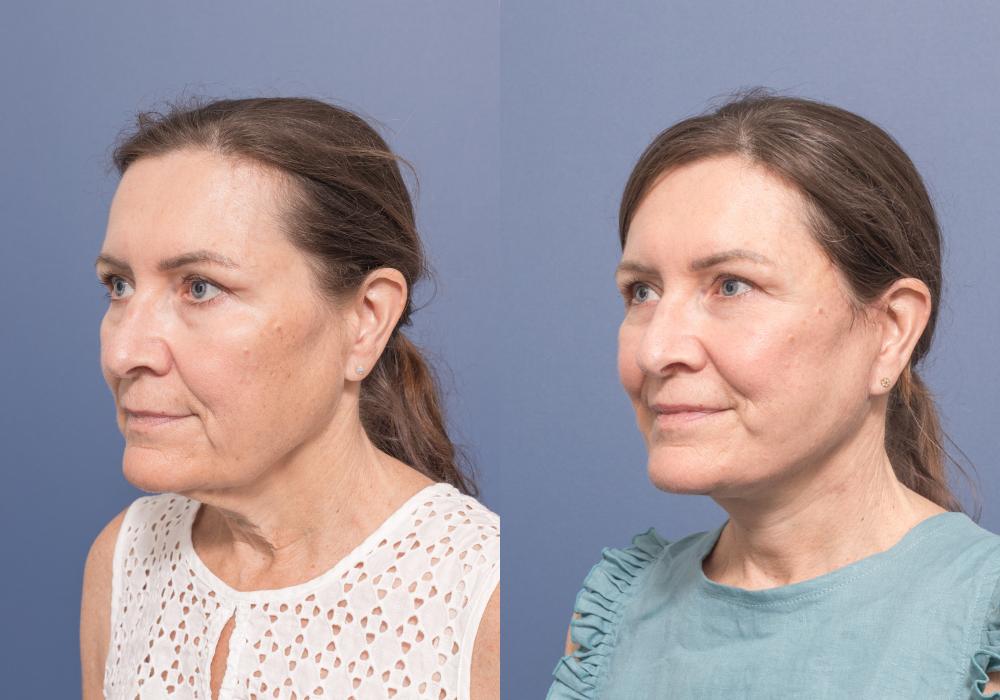
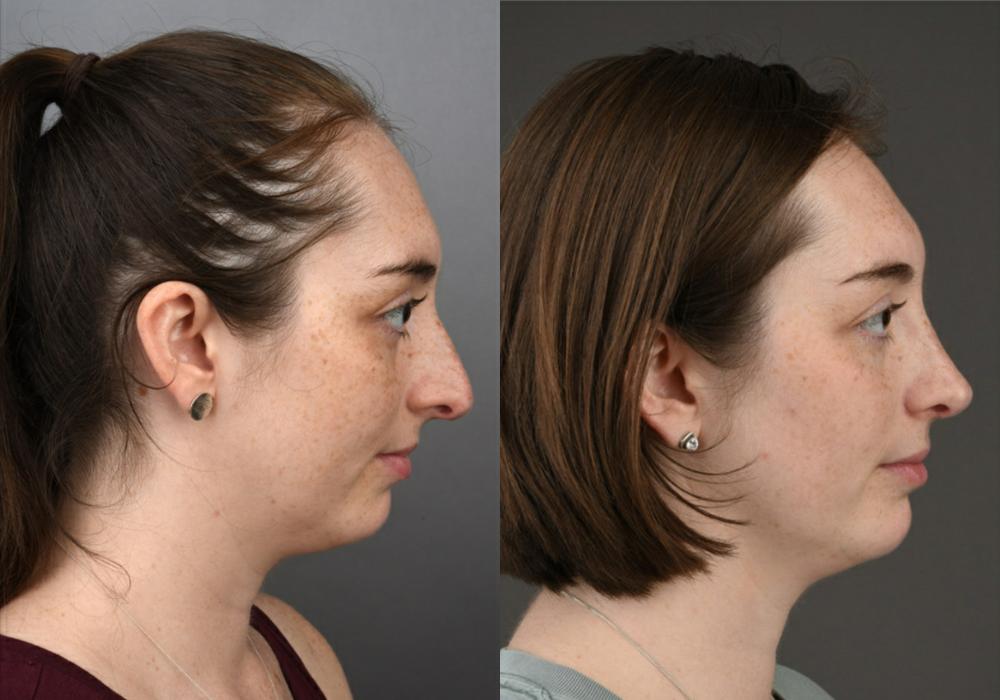
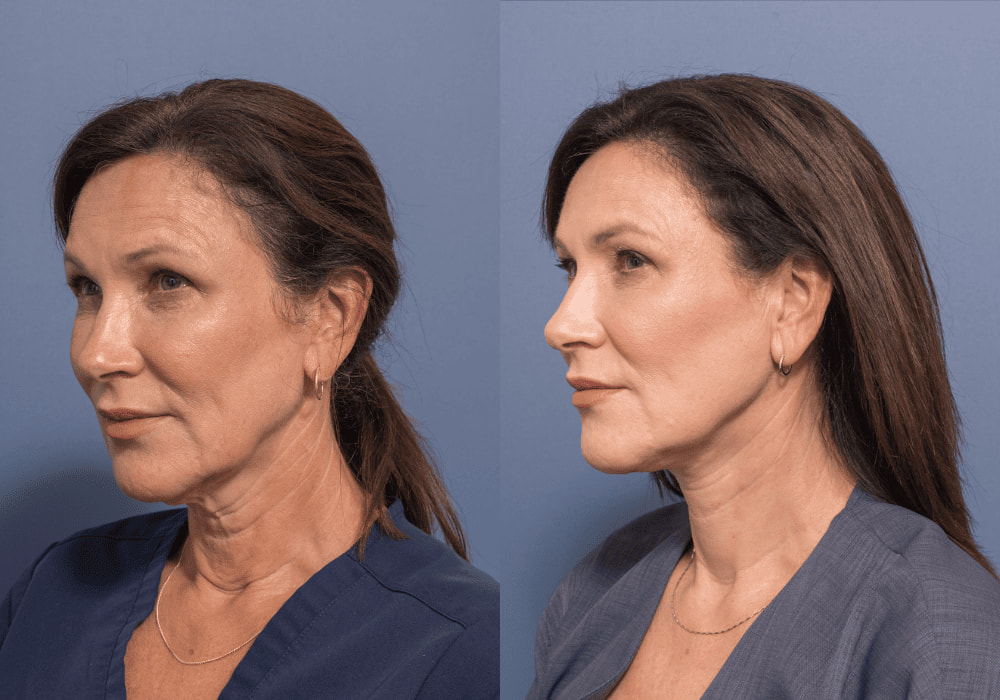
In contrast, the deep plane facelift technique repositions the sagging muscles and fat of the face as a unit, without separating the skin from the underlying soft tissues. This approach offers a more natural and long-lasting result.
Traditional facelift techniques also typically involve tightening the face horizontally, resulting in an artificial and stretched appearance that can affect the corners of the lips and create a windswept look.

In contrast, the deep plane technique involves redraping the tissues in a vertical vector to lift the lower face in a way that produces a smoother and more natural outcome.

The deep plane technique can also help restore volume to the cheeks, elevate sagging in the corners of the mouth, and reduce the appearance of nasolabial folds and marionette lines.
Note: Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risk. These risks will be discussed with you in detail during the consultation. For further information on risks please refer to the patient resources section of the website.