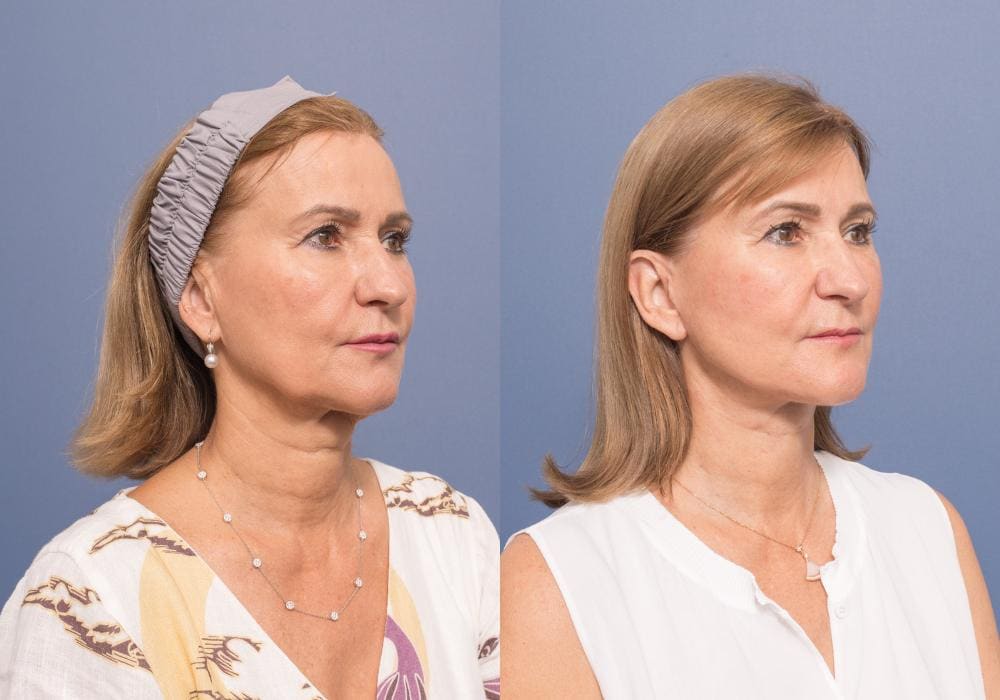
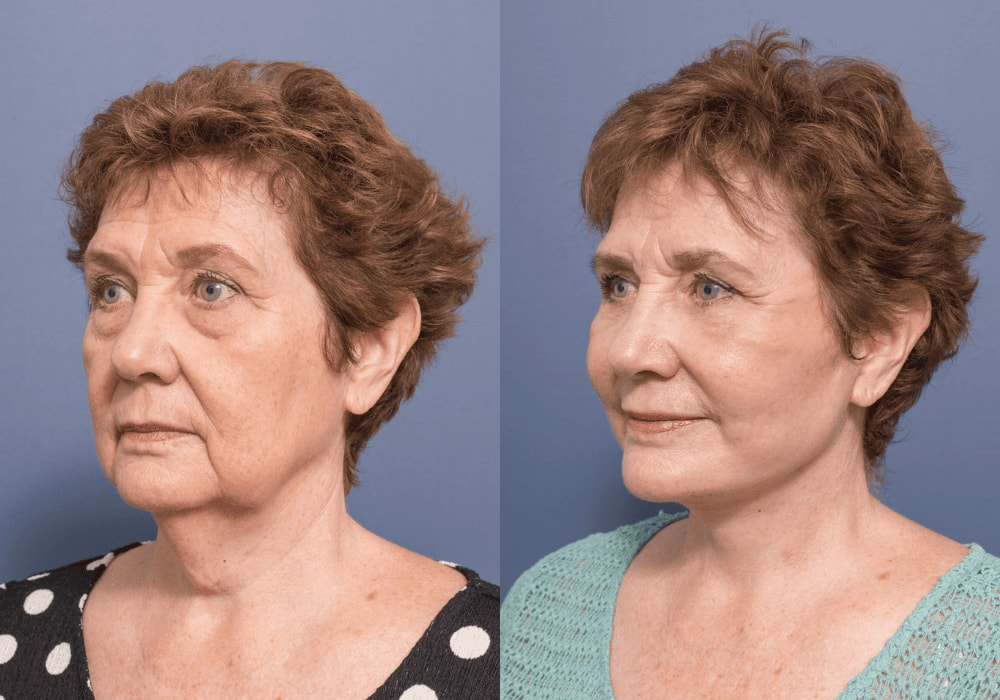
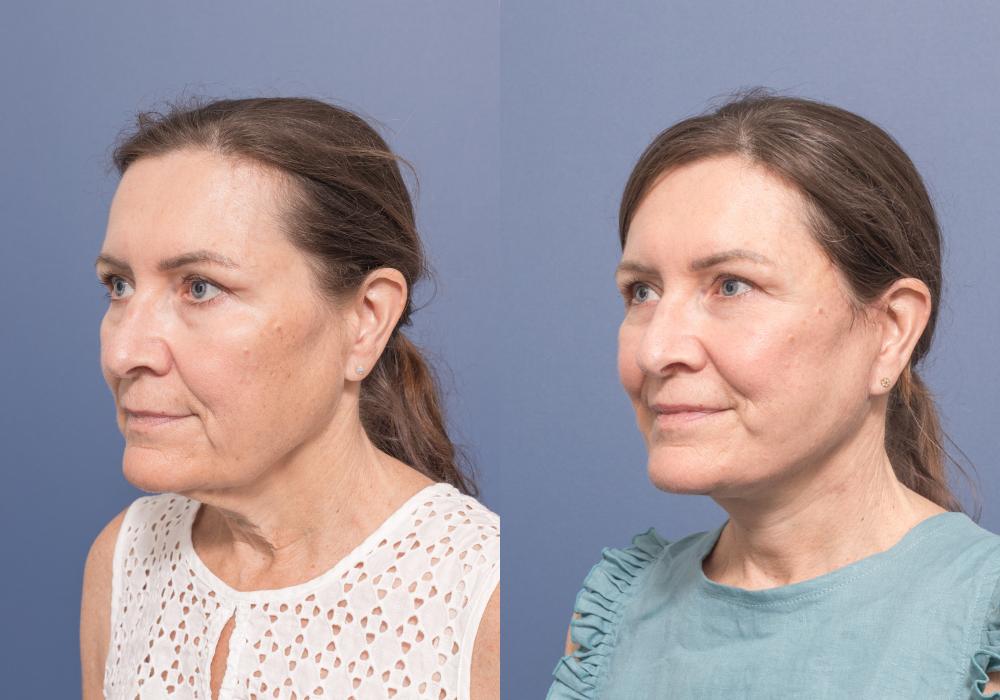
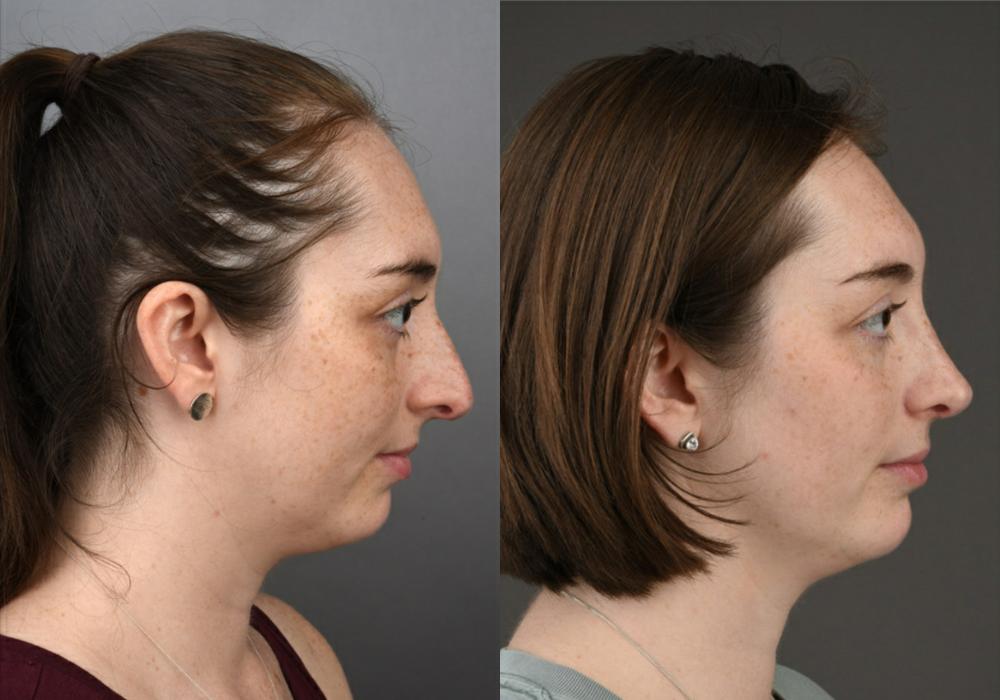
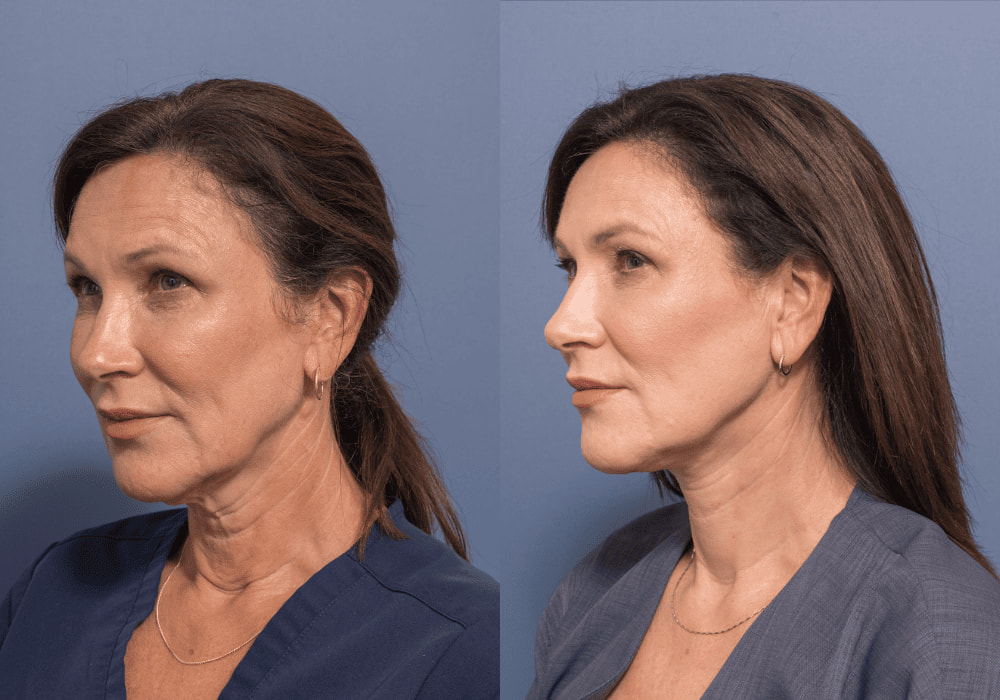
A revision facelift is a surgical procedure performed to improve the results of a previous facelift. Revision facelifts can address various issues that may have occurred following a previous facelift, including skin laxity, scarring, asymmetry, and unnatural results.
Revision Face and Neck Lift: If you are unhappy with a previous facelift or want a refresh, consider a revision face or neck lift!
Why do some facelifts fail?
Many factors can contribute to the failure of a facelift, including over-tightening of the skin, inadequate facial ligament release and tissue repositioning, inadequate skin removal, and the use of outdated techniques.
One of the most common reasons for a facelift to fail is the use of lateral superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) techniques, which are not durable.
Why traditional SMAS facelifts are not long lasting
SMAS plication and imbrication techniques involves lifting the skin and tightening the lateral fixed SMAS without release of the facial retaining ligaments or deeper soft tissues of the lower face and neck. Lateral SMAS type facelifts can produce a temporary improvement in facial appearance, however, lateral SMAS techniques do not address deeper layers of the face, which contributes to soft tissue redundancy in the lower face and neck and this is why Dr. Honeybrook does not use lateral SMAS type facelifts and instead opts for a deep plane facelift technique.
What is the typical duration of a deep plane facelift
Although a facelift can produce dramatic results, they are not permanent, even if performed well. As time passes, the facial skin may start to sag again, and the underlying soft tissues may droop. Typically, a well performed deep plane facelift can last for around 10 to 15 years before the effects begin to diminish.When the outcomes of a facelift start to fade, patients may choose to undergo a revision procedure.
What is the recommended waiting period before undertaking a revision facelift?
Patients who wish to undergo a second facelift should wait for a minimum of 12 months following their first surgery. It takes approximately one year for the skin, muscles, and other tissues to heal adequately, allowing the face to withstand another operation.
The complexities of revision facelifting
Revision facelifts are often more complex than primary facelifts due to the presence of scar tissue and the altered anatomy resulting from the previous surgery. Surgeons performing revision facelifts must have advanced training and experience in order to achieve optimal results.
Why a deep plane facelift?
Dr. Honeybrook performs a deep plane facelift for revision facelifts as this technique involves repositioning the deeper layers of facial tissue, allowing for a more natural-looking and longer-lasting result. This technique is particularly effective for patients who have previously had a lateral SMAS type facelift as the prior surgeon has unlikely dissected the deep plane. This undissected tissue can then be safely elevated in a similar fashion to a primary facelift, without significant risk to the underlying nerves.
Recovery after a revision facelift
Recovery after a revision facelift is similar to that of a primary facelift. Patients will experience bruising and swelling for 2-3 weeks after surgery, which will gradually subside. Dr. Honeybrook will provide specific post-operative instructions to help patients recover safely and comfortably.
Who are good candidates for a revision facelift?
Good candidates for a revision facelift are individuals who have previously undergone a facelift, but are unhappy with the results or have experienced complications. Individuals should be in good health, have realistic expectations, and have a clear understanding of the potential risks and benefits of the procedure. A consultation with Dr. Honeybrook will determine whether a revision facelift is the best option for each individual.
Note: Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risk. These risks will be discussed with you in detail during the consultation. For further information on risks please refer to the patient resources section of the website.