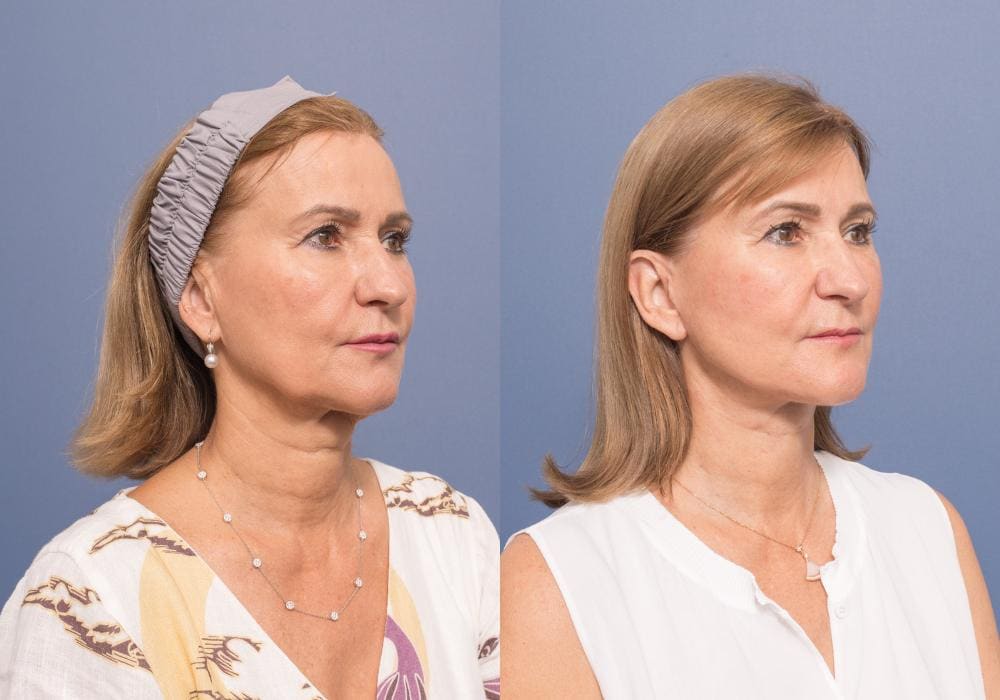
A septal perforation is a hole in the nasal septum, which is the cartilage and bone that separates the two nostrils
Septal Perforation Repair: A safe and effective method for repairing holes in your nasal septum that separates your nostrils
Common causes of a septal perforation
The most common causes of septal perforations are trauma to the nose, including nose-picking, drug use, and previous nasal surgeries. However, other causes include chronic nasal inflammation, infections, and autoimmune diseases.
Symptoms of a septal perforation
Symptoms of a septal perforation can include nasal crusting, frequent nosebleeds, a whistling sound while breathing, and a decreased sense of smell. Individuals may also experience subjective difficulty in breathing and have a feeling of dryness in their nose.
Repairing a septal perforation
There are many methods of repairing a septal perforation, including various types of flaps, cartilage and fascial grafts. Dr. Adam Honeybrook specialises in two main techniques for repairing larger septal perforations: temporoparietal fascia wrapped around cartilage or bioabsorbable plate, and the anterior ethmoid artery flap.
Fascial repair
The temporoparietal fascia wrapped around cartilage or bioabsorbable plate involves using tissue from the individual’s own body to repair the septal perforation. The temporoparietal fascia is a layer of tissue located on the side of the head, near the temple. This technique involves harvesting a small section of this fascia and wrapping it around a segment of cartilage or a bioabsorbable plate.
During the surgery, an open rhinoplasty approach is often used to access the nasal septum. An open rhinoplasty approach involves making a small incision on the columella (the tissue between the nostrils) and lifting the skin and soft tissues off the underlying nasal structures. This allows the surgeon to see the septal perforation and repair it using the temporoparietal fascia and cartilage or bioabsorbable plate graft.
The advantage of this technique is that it uses the individual’s own vascularised tissue as a scaffold to close the perforation, which reduces the risk of rejection or infection. This technique can be used for larger septal perforations up to 3cm in diameter.
Nasal flaps
The anterior ethmoid artery flap technique involves using a flap of tissue from the individual’s internal nasal cavity to repair a septal perforation. This technique involves making an incision on the inside of the nose and elevating a flap of tissue supplied by anterior ethmoid artery, which is a blood vessel located in the nasal cavity.
The flap is then rotated into the septal perforation and sutured in place. This technique can be used for smaller septal perforations and has the advantage of using tissue from the same area as the perforation.
Overall, both techniques have shown success rates ranging from 85% to 95% in the literature. The choice of technique will depend on the size and location of the septal perforation, as well as the individual’s individual needs and preferences. Dr. Honeybrook will work closely with each individual to determine the best treatment for their specific case.
Recovery after septal perforation repair
Individuals can expect to have prolonged internal nasal splinting after the procedure to protect the healing tissues. They may also experience swelling and bruising for several months if an open rhinoplasty approach is used. Most individuals can return to normal activities within two weeks after the surgery.
Who are candidates for septal perforation repair?
Good candidates for septal perforation repair include individuals who experience significant symptoms such as chronic nasal crusting, nosebleeds, and whistling. Also, young patients with an asymptomatic smaller hole may be candidates for repair as there is risk of the hole enlarging with time.
Note: Any surgical or invasive procedure carries risk. These risks will be discussed with you in detail during the consultation. For further information on risks please refer to the patient resources section of the website.